The Growing Market for Tunable Lasers
The world is moving towards tunability. The combination of tunable lasers and dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM) allows datacom and telecom industries to expand their network capacity without increasing their existing fiber infrastructure. Furthermore, the miniaturization of coherent technology into pluggable transceiver modules has finally enabled the widespread implementation of IP over DWDM solutions.
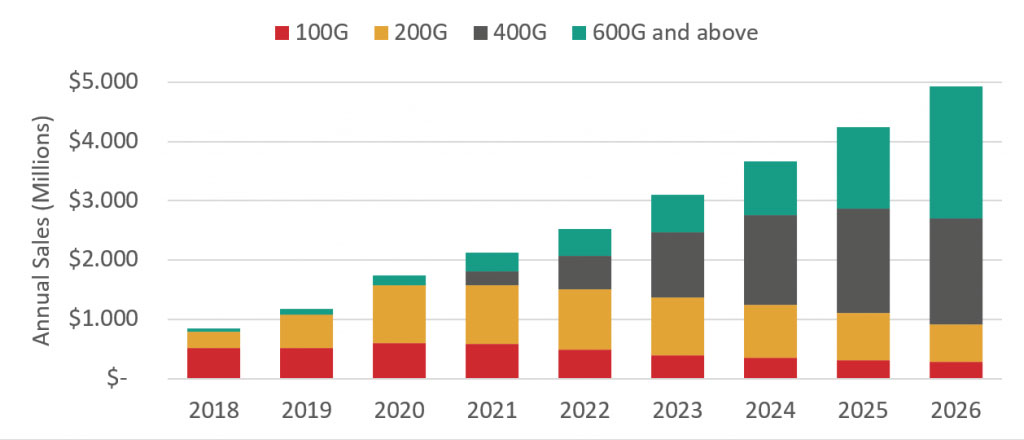
Self-tuning algorithms have also made DWDM solutions more widespread by simplifying their installation and maintenance. Hence, many application cases—metro transport, data center interconnects, and even future access networks—are moving towards coherent tunable pluggables. The market for coherent tunable transceivers will explode in the coming years, with LightCounting estimating that annual sales will double by 2026. Telecom carriers and especially data center providers will drive the market demand, upgrading their optical networks with 400G, 600G, and 800G pluggable transceiver modules that will become the new industry standards.
Same Laser Performance, Smaller Package
As the industry moves towards packing more and more transceivers on a single router faceplate, tunable lasers need to maintain performance and power while moving to smaller footprints and lower power consumption and cost. Due to the faceplate density requirements for data center applications, transceiver power consumption is arguably the most critical factor in this use case.
In fact, power consumption is the main obstacle preventing pluggables from becoming a viable solution for a future upgrade to Terabit speeds. Since lasers are the second biggest power consumers in the transceiver module, laser manufacturers faced a paradoxical task. They must manufacture laser units that are small and energy-efficient enough to fit QSFP-DD and OSFP pluggable form factors while maintaining the laser performance. Fortunately, these ambitious spec targets became possible thanks to improved photonic integration technology.
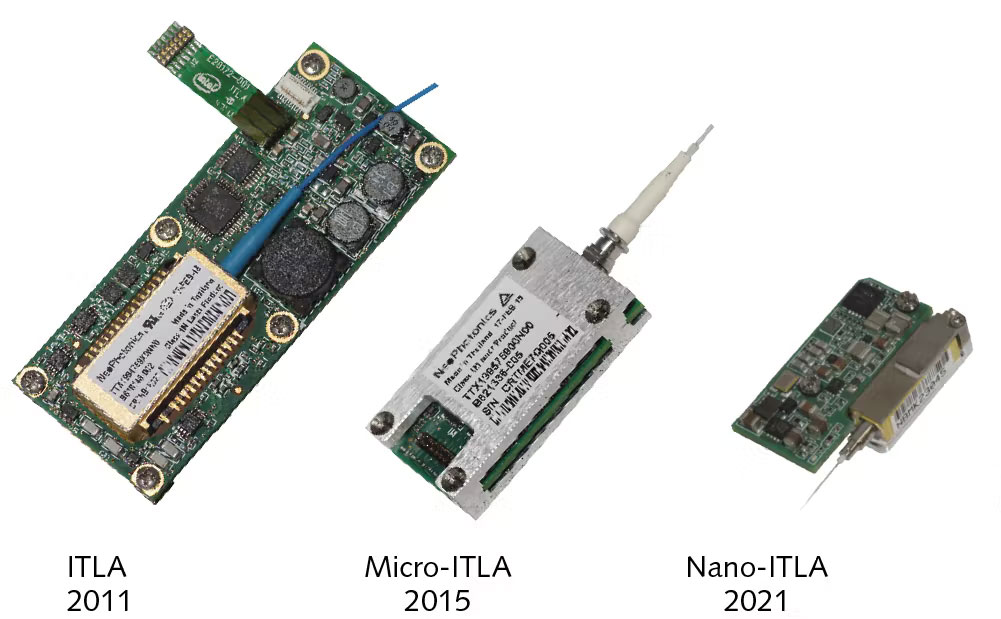
The original 2011 ITLA standard from the Optical Internetworking Forum (OIF) was 74mm long by 30.5mm wide. By 2015, most tunable lasers shipped in a micro-ITLA form factor that cut the original ITLA footprint in half. In 2021, the nano-ITLA form factor designed for QSFP-DD and OSFP modules has once again cut the micro-ITLA footprint almost in half. The QSFP-DD modules that house the full transceiver are smaller (78mm by 20mm) than the original ITLA form factor. Stunningly, tunable laser manufacturers achieved this size reduction without impacting laser purity and power.
Versatile Laser Developers for Different Use Cases
The different telecom and datacom applications will have different requirements for their tunable lasers. Premium coherent systems used for submarine and ultra-long-haul require best-in-class lasers with the highest power output and purity. On the other hand, metro transport and data center interconnect applications do not need the highest possible laser quality, but they need small devices with lower power consumption to fit router faceplates. Meanwhile, the access network space looks for lower-cost components that are also temperature hardened.
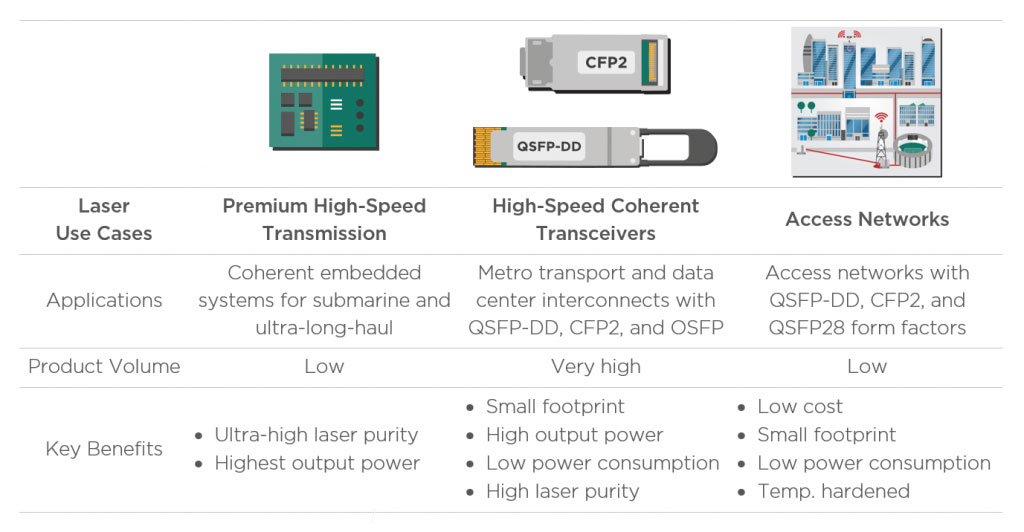
These varied use cases provide laser developers with ample opportunities and market niches to provide fit-for-purpose solutions for. For example, a laser module can be set to run at a higher voltage to provide higher output power and reach for premium long-haul applications. On the other hand, tuning the laser to a lower voltage would enable a more energy-efficient operation that could serve more lenient, shorter-reach use cases (links < 250km), such as data center interconnects.
An Independent Player in Times of Consolidation
With the increasing demand for coherent transceivers, many companies have performed acquisitions and mergers that allow them to develop transceiver components internally and thus secure their supply. LightCounting forecasts show that while this consolidation will decrease the sales of modulator and receiver components, the demand for tunable lasers will continue to grow. The forecast expects the tunable laser market for the transceiver to reach a size of $400M in 2026.
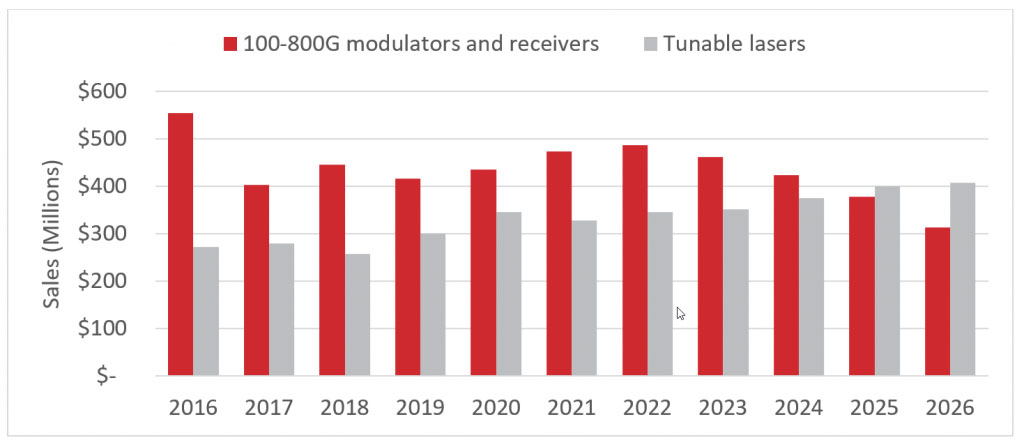
We can dive deeper into the data to find the forces that drive the steady growth of the laser market. As shown in Figure 4, the next five years will likely see explosive growth in the demand for high-purity, high-power lasers. The forecast predicts that the shipments of such laser units will increase from roughly half a million in 2022 to 1.4 million in 2026 due to the growth of 400G and 800G transceiver upgrades. However, the industry consolidation will make it harder for component and equipment manufacturers to source lasers from independent vendors for their transceivers.
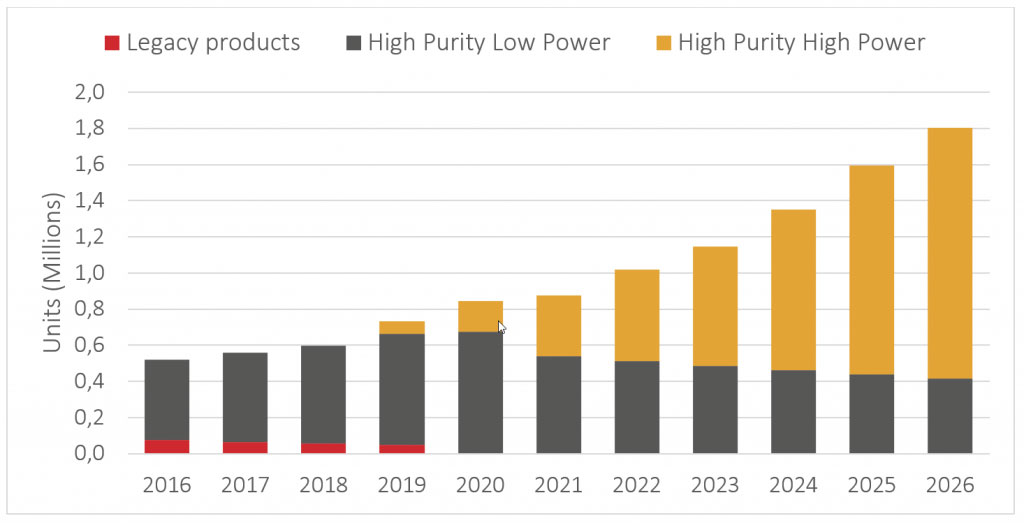
This data indicates that the market needs more independent vendors to provide high-performance ITLA components that adapt to different datacom or telecom provider needs. Following these trends, at EFFECT Photonics, we are not only developing the capabilities to provide a complete coherent transceiver solution but also the nano-ITLA units needed by other vendors.
Takeaways
The world is moving towards tunability. As telecom and datacom industries seek to expand their network capacity without increasing their fiber infrastructure, the sales tunable transceivers will explode in the coming years. These transceivers need tunable lasers with smaller sizes and lower power consumption than ever. Fortunately, the advances in photonic integration are managing to fulfill these laser requirements, leading to the new nano-ITLA module standards. However, even though component and equipment vendors need these tunable lasers for their next-gen transceivers, the industry consolidation can affect their supply. This situation presents an opportunity for new independent vendors to supply nano-ITLA units to this growing market.
